Social and Economic Effects
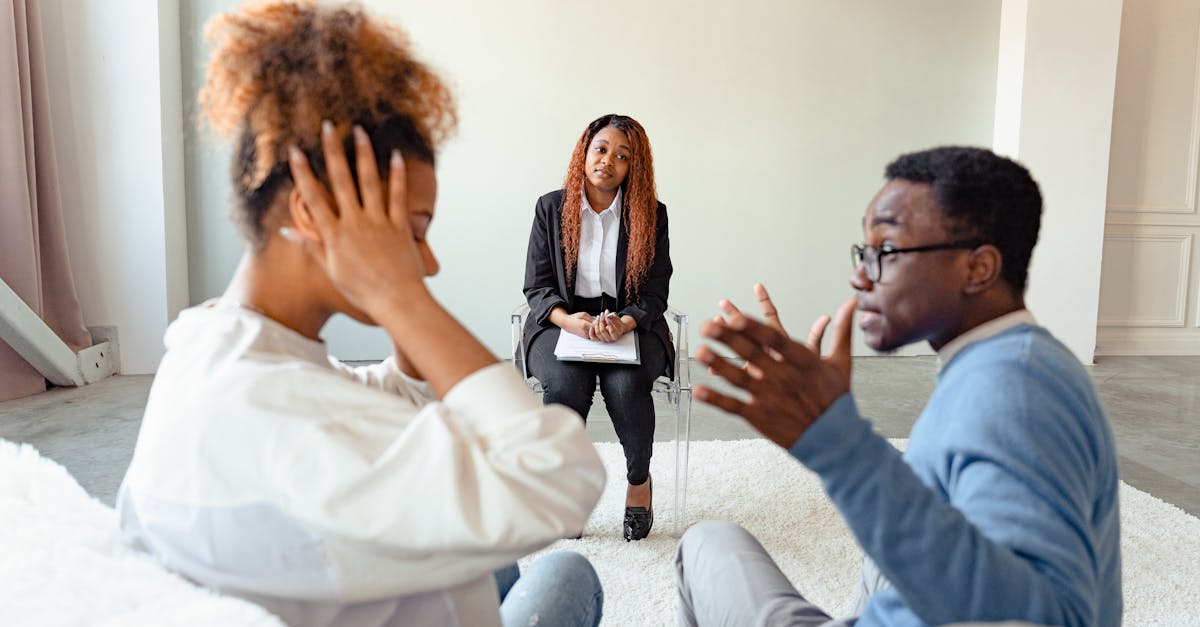
Substance abuse can have profound social effects that ripple through communities, affecting relationships and social stability. Families often bear the brunt of the consequences, experiencing disruptions in communication, trust, and emotional well-being. Friends and neighbors may feel compelled to intervene, which can sometimes lead to strained relationships or further isolation for those struggling with addiction. Additionally, public spaces may become less safe as substance abuse increases, leading to concerns about crime and disorder.
The economic effects of substance abuse are equally significant, impacting both individuals and the larger community. Employers face increased costs due to absenteeism, decreased productivity, and higher turnover rates among employees affected by substance abuse. Healthcare systems also bear the burden, as they must allocate resources to treat individuals suffering from related health complications. Communities may experience reduced economic growth due to diminished workforce participation and increased reliance on social services, creating a cycle that can be difficult to break.
How Substance Abuse Affects Communities
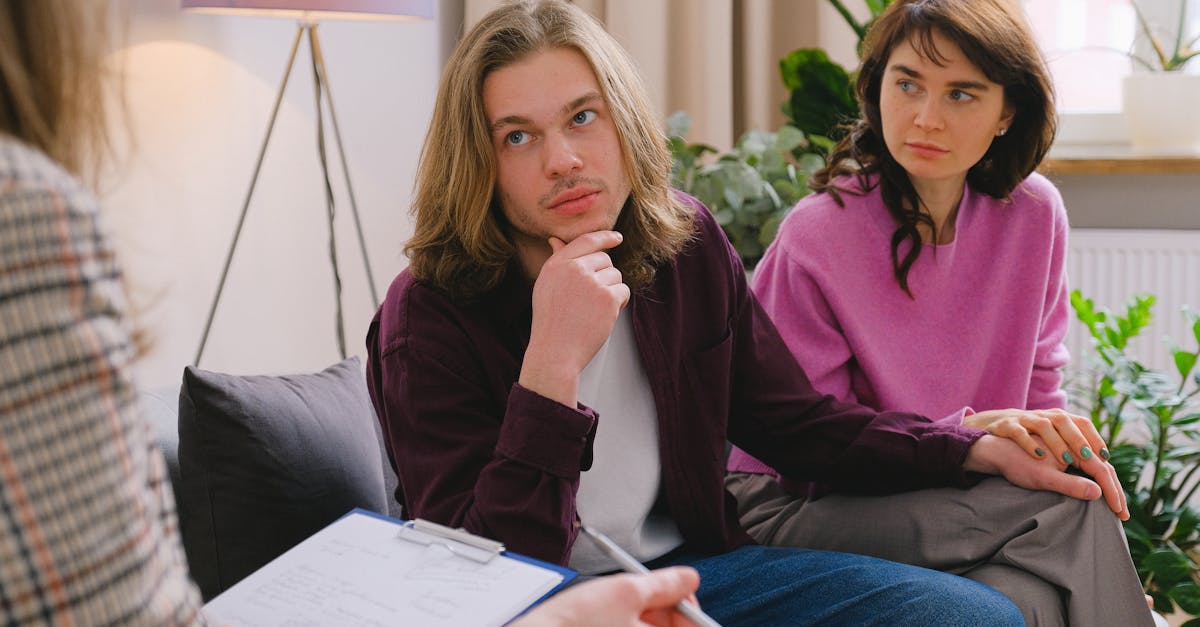
Substance abuse can have far-reaching impacts on communities, affecting various aspects of social life. Increased crime rates often accompany higher levels of substance abuse, leading to safety concerns. Neighborhoods may experience a decline in property values due to drug-related activities. Strained public resources such as healthcare and law enforcement can become overwhelmed as communities struggle to address the consequences of substance abuse. This creates a cycle where present challenges make it harder to attract new businesses and families.
In addition to economic ramifications, substance abuse undermines community cohesion. Families may face significant turmoil, resulting in higher rates of domestic violence and family breakdowns. The stigma surrounding substance abuse can alienate individuals, reducing community engagement and support. As schools and local organizations grapple with the fallout, educational opportunities and youth programs may suffer. Communities that cannot effectively address substance abuse may find themselves trapped in a cycle of poverty and social disarray.
Treatment Options
Treating substance abuse involves a variety of approaches tailored to individual needs. These options can range from outpatient therapy to residential treatment programs. Many individuals benefit from a combination of counseling, medication management, and support groups. Behavioral therapies play a crucial role in helping individuals change their patterns of thinking and behavior related to substance use. Additionally, medications such as methadone or buprenorphine are often used to help manage withdrawal symptoms and cravings for substances like opioids.
Incorporating holistic methods can enhance the recovery process for those dealing with substance abuse. Options such as mindfulness, yoga, and art therapy provide additional tools for coping with the emotional and psychological challenges of recovery. Some treatment programs emphasize life skills training to prepare individuals for everyday challenges without resorting to substance use. Continuous support through aftercare programs is vital in maintaining long-term sobriety and preventing relapse. The journey to recovery is multifaceted, involving medical, psychological, and social components that work together to support individuals in their path to healing.
Approaches to Recovery
Approaches to recovery from substance abuse vary widely depending on individual circumstances and the substances involved. One common method is outpatient treatment, which allows individuals to maintain their daily routines while receiving support and therapy. This model offers flexibility and accessibility, making it suitable for those who might not require 24-hour supervision. In contrast, residential treatment programs provide a structured environment that immerses individuals in recovery-focused activities and therapies. Such programs can be essential for those with severe addiction, offering a safe space free from external triggers.
Support groups play a critical role in many recovery journeys. These groups foster a sense of community and connection, enabling individuals to share their experiences and challenges in a nonjudgmental setting. Programs like Alcoholics Anonymous and Narcotics Anonymous have proven effective for many, helping individuals stay accountable while learning from others who have faced similar struggles. Additionally, therapeutic approaches such as cognitive-behavioral therapy can equip individuals with coping strategies, helping them address the underlying issues that contribute to substance abuse.
Prevention Strategies
Prevention strategies are essential for addressing substance abuse effectively. Education plays a crucial role in empowering individuals with knowledge about the risks associated with drug and alcohol use. Programs that promote awareness in schools and community centers can help dispel myths and provide accurate information. By engaging families and fostering open discussions, these initiatives create supportive environments that discourage substance abuse among youth.
Community involvement significantly enhances prevention efforts. Local organizations can collaborate to create programs that address specific risk factors within neighborhoods. Activities such as workshops, recreational events, and counseling sessions can strengthen ties among community members and encourage a culture of healthy choices. When individuals feel connected and supported, the likelihood of engaging in substance abuse decreases, paving the way for stronger, more resilient communities.
Effective Ways to Reduce Risk
To effectively reduce the risk of substance abuse, community and individual education plays a crucial role. Programs that provide accurate information about the dangers associated with various substances can empower people to make informed choices. Schools, workplaces, and community centers can host workshops and discussions that focus on the long-term effects of substance use. These educational initiatives can target both young people and adults, creating a broader awareness of the issue.
Another important strategy is fostering supportive environments that encourage healthy lifestyles. Constructive engagement in activities such as sports, arts, and volunteer work can help individuals build resilience against substance abuse. By promoting social connections and proactive coping mechanisms, people are less likely to resort to drugs or alcohol as a means of escape. Comprehensive support networks can also be established to provide resources and encouragement for those facing challenges related to substance use.
FAQS
What is substance abuse?
Substance abuse refers to the harmful or hazardous use of psychoactive substances, including alcohol and illicit drugs, which leads to significant adverse consequences in various aspects of an individual's life.
What are the common signs of substance abuse?
Common signs of substance abuse can include changes in behavior, neglecting responsibilities, withdrawal from social activities, mood swings, and physical symptoms such as weight loss or poor hygiene.
How does substance abuse affect individuals and families?
Substance abuse can lead to a range of negative effects on individuals and families, including strained relationships, financial difficulties, legal problems, and a decline in physical and mental health.
What treatment options are available for substance abuse?
Treatment options for substance abuse often include therapy (such as cognitive-behavioral therapy), support groups, medication-assisted treatment, and inpatient or outpatient rehabilitation programs.
How can communities prevent substance abuse?
Communities can prevent substance abuse by implementing education programs, promoting healthy lifestyle choices, providing access to mental health resources, and creating support systems for those at risk.